Texas Connector Pipeline Seeks Route Cuts, Compressor Upgrades in FERC Filing
(P&GJ) — Texas Connector Pipeline LLC has filed an application with the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) to amend its plans for a natural gas pipeline project in Jefferson and Orange Counties, Texas.
The filing, submitted on Aug. 12, requests approval to modify certain facilities, including major changes to the pipeline’s routing and compression capacity.
The Texas Connector Pipeline is part of the Port Arthur Liquefaction Project, which was authorized by FERC in 2019. However, with ongoing developments and landowner requests, Texas Connector now seeks to adjust the pipeline's design to improve efficiency and constructability. This includes changes to both the Southern and Northern segments of the pipeline, as well as alterations to the Orangefield Compressor Station, which is located in the project's northern section.
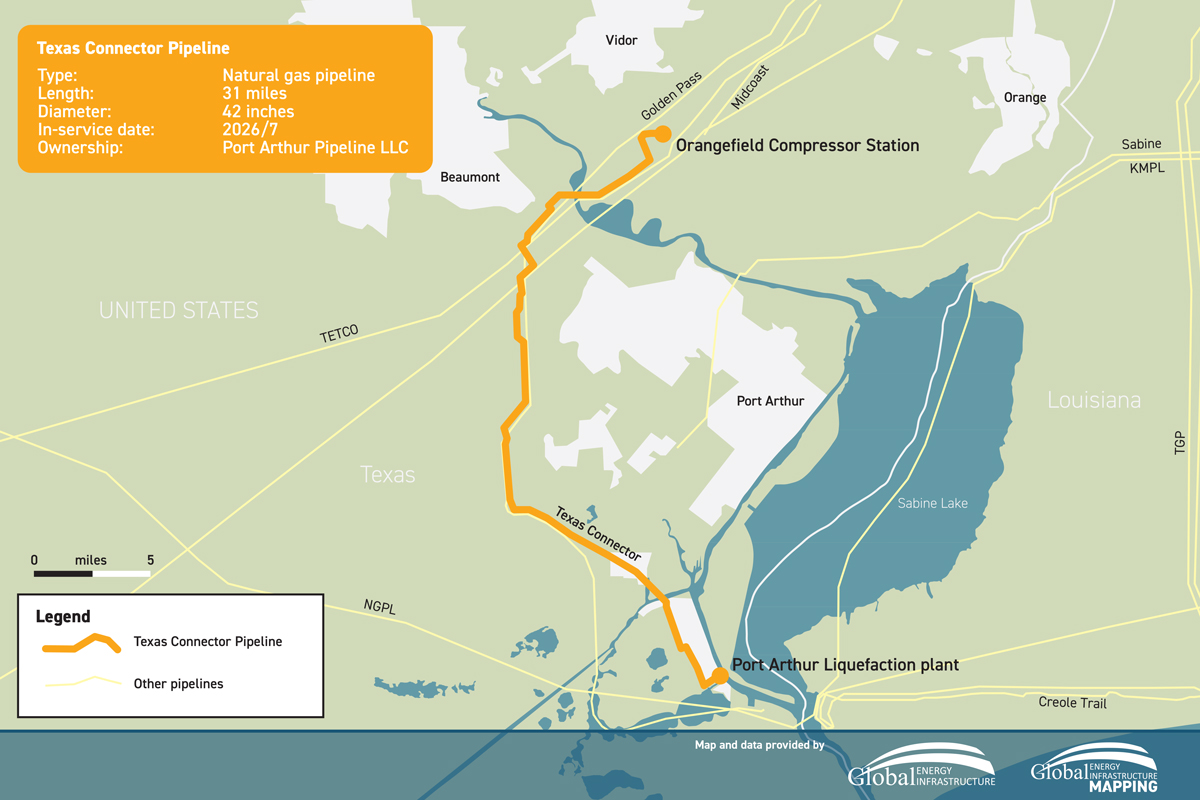
Pipeline Route and Information
For an overview of this project and other related infrastructure developments, visit Global Energy Infrastructure.
Under the proposed amendments, the Southern Segment of the pipeline will be shortened significantly, reducing its length from 7.6 miles to just 1.4 miles. Additionally, the planned Southern Compressor Station will no longer be constructed, with its designated site repurposed for a laydown yard and access road. Meanwhile, the Northern Segment of the pipeline will see a slight extension, growing from 26.6 miles to 29.6 miles, as the project adjusts to new landowner requirements and development within the existing right-of-way.
At the Orangefield Compressor Station, Texas Connector plans to increase compression capacity by replacing the originally planned three natural gas-driven turbines with four new, more powerful SolarTitan 130 Gas Turbine compressors. These changes would increase the station's total capacity, significantly boosting the pipeline's ability to transport natural gas.
The modification request also includes new water access routes, such as dredging Big Hill Bayou to allow for vessel transit. These measures are expected to help the project meet its goals while minimizing environmental disruption.
FERC has announced that an Environmental Assessment (EA) will be conducted, with the document expected to be issued in March 2025. The review process will include a 30-day comment period, during which the public and interested parties can submit feedback. A decision on federal authorizations for the project is expected by June 2025, following the completion of the environmental review.
As of December 2024, no comments have been received from stakeholders following the project's scoping period, which concluded in November. The commission also noted that no agencies have volunteered to assist with the environmental review, though all substantive issues identified by staff will be addressed in the EA.
These amendments to the Texas Connector Pipeline are part of the ongoing effort to streamline the project and adjust to evolving construction needs. As the approval process continues, both local stakeholders and broader environmental groups will have the opportunity to weigh in on the proposed changes.
In a Nov. 25 filing, FERC noted plans to prepare the environmental document for the amendment. The proposed updates, including changes to pipeline lengths, compressor station configurations, and new water access routes, aim to address landowner requests and operational needs.
The project’s footprint is expected to increase by 95.6 acres for construction and 94.8 acres for permanent operations.
The Author
Related News
Related News

- Energy Transfer to Build $5.3 Billion Permian Gas Pipeline to Supply Southwest
- Enbridge Sees High Demand to Expand 593-Mile Canada-to-U.S. Gulf Oil Pipeline
- Strike Pioneers First-of-Its-Kind Pipe-in-Pipe Installation on Gulf Coast with Enbridge
- 208-Mile Mississippi-to-Alabama Gas Pipeline Moves Into FERC Review
- Chesapeake, AEP to Build $10 Million Ohio Gas Pipeline for Data-Center Power
- 275-Mile Texas-to-Oklahoma Gas Pipeline Enters Open Season
- Enbridge Sees High Demand to Expand 593-Mile Canada-to-U.S. Gulf Oil Pipeline
- LNG Canada Start-Up Fails to Lift Gas Prices Amid Supply Glut
- Strike Pioneers First-of-Its-Kind Pipe-in-Pipe Installation on Gulf Coast with Enbridge
- Trump Claims Japan, U.S. to Form Joint Venture for Alaska LNG Exports





Comments