August 2022, Vol. 249, No. 8
Features
DIMP Still Providing Pipeline Replacement Jobs
(P&GJ) — The level of work to replace cast iron and bare steel pipe has decreased in volume since 2009, when it was introduced. However, the Gas Distribution Integrity Management Program (DIMP) still requires a significant amount of construction work.
The U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT) estimated that at the end of 2021, 38,403 miles (61,804 km) of bare steel and 18,031 miles (29,018 km) of cast iron pipelines were still in service in the United States Most of this pipe is in eastern cities with older infrastructure systems, such as New York, Boston, Washington, D.C. and Philadelphia.
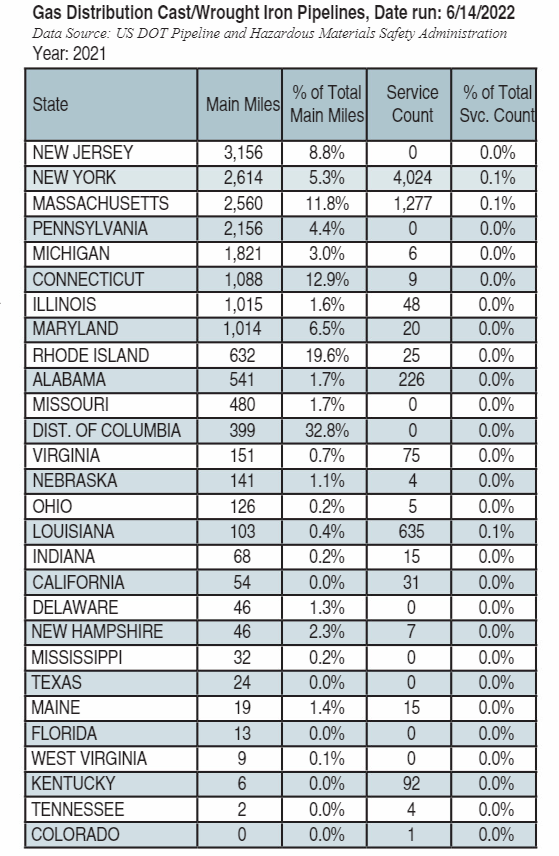
Among individual states, New Jersey led the way with 3,156 miles (5,079 km) of cast iron, followed by New York (2,614 miles [4207 km]), Massachusetts (2,560 miles [4,120 km]), Pennsylvania (2,156 miles [3,470 km]) and Michigan (1,821 miles [2,931 km]).
States with the most bare steel mains were Ohio (5,547 miles [8,927 km]), Pennsylvania (5,499 miles [8,850 km]), New York (4,522 miles [7,277 km]) and Texas (4,022 miles [6,473 km]).
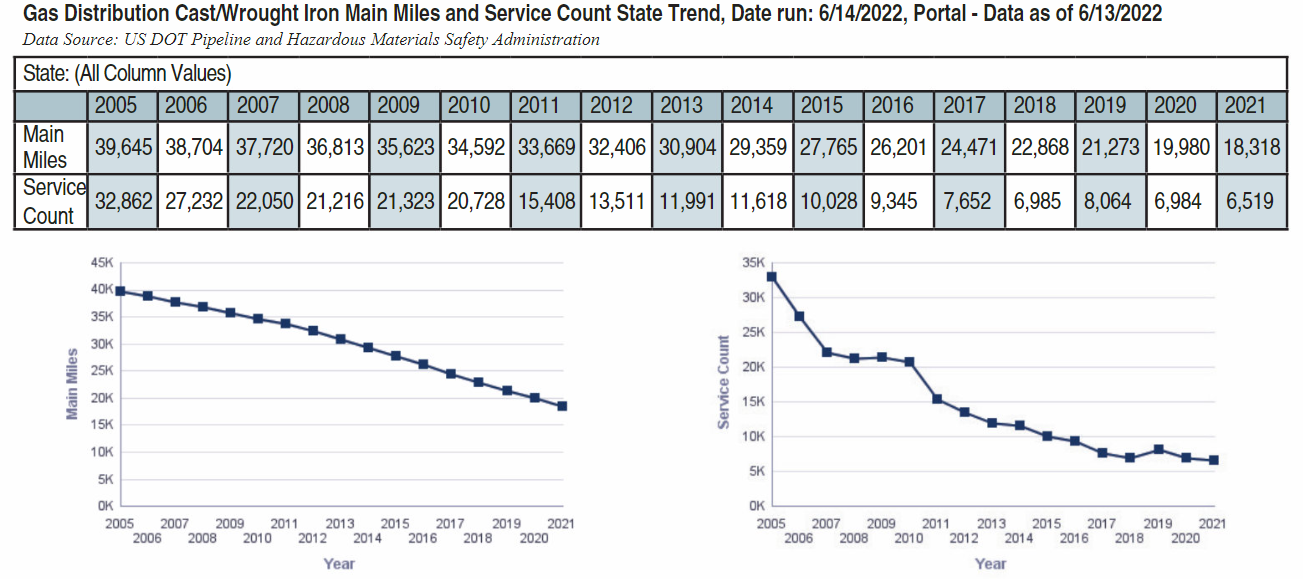
Further DOT data indicate that replacement work, while progressing steadily for more than a decade now, is far from complete. In 2015, there were still 27,771 miles (44,693 km) of wrought and cast iron gas distribution lines in service in the U.S., down from 39,342 miles (63,315 km) since 2005, a decrease of almost 30%.
According to the Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration (PHMSA), about 97% of natural gas distribution pipelines in the U.S. were made of plastic or steel at the end of 2020. The remaining 3% is primarily cast iron pipe.
Cast and wrought iron pipelines were originally constructed to transport manufactured gas beginning in the 1870s and 1880s, with cast iron becoming more popular in the early 1900s.
In 1970, PHMSA began collecting data about gas pipelines mileage categorized by pipe material type. In 1983, gas distribution pipeline operators reported 61,536 miles (99,033 km) of cast iron and 4,371 miles (7,034 km) of wrought iron pipe. Operators began submitting merged data for the two beginning in 1984.
In late 2009, PHMSA implemented pipeline safety regulations for managing the integrity of gas distribution pipelines. Operators were required to create DIMP by August 2011. Operators are required to know the specific characteristics of their system and operating environment to identify threats, evaluate the risk and take measures to reduce the risk.





Comments